sui
安装
https://docs.sui.io/guides/developer/getting-started/sui-install
windows直接choco install sui就好了
连接到sui本地网络
每次执行sui-test-validator都是新开一个网络,没有之前的数据
访问本地节点,成功回显:
ubuntu@VM-16-7-ubuntu:~/sui/target/release$ curl --location --request POST 'http://127.0.0.1:9000' \ > --header 'Content-Type: application/json' \ > --data-raw '{ > "jsonrpc": "2.0", > "id": 1, > "method": "sui_getTotalTransactionBlocks", > "params": [] > }' {"jsonrpc":"2.0","result":"2","id":1}
管理网络
- 切换网络:
sui client switch --env [network alias] - 默认网络别名:
- 本地网 localnet: http://0.0.0.0:9000
- 开发网 devnet: https://fullnode.devnet.sui.io:443
- 测试网 testnet: https://fullnode.testnet.sui.io:443
- 列出当前所有网络别名:
sui client envs - 添加新的网络别名:
sui client new-env --alias <ALIAS> --rpc <RPC>
查询启用地址和 Gas Objects
- 查询当前保存了密钥的地址:
sui client addresses - 查询当前启用的地址:
sui client active-address - 列出所拥有的 gas objects:
sui client gas - 查询余额:
sui client balance
获取token
在discord频道发消息
或者
curl --location --request POST 'https://faucet.testnet.sui.io/gas' \ --header 'Content-Type: application/json' \ --data-raw '{ "FixedAmountRequest": { "recipient": "<YOUR SUI ADDRESS>" } }'
sui cli
导出私钥
命令行创建的默认钱包,使用sui keytool export --key-identity <suiAddress>可以得到以suiprivkey开头的私钥
Package
新建:sui move new <xxxx>
测试:sui move test或者sui move test <xxxx>,后者测试名字包含xxxx的
发布:sui client publish --gas-budget 100000000
发布后init返回的object id会在object changes - created objects里体现
call
#调用一个没有参数的函数 sui client call [OPTIONS] --package <package id> --module <module名称> --function <函数名> --gas-budget <GAS_BUDGET> #调用带参数的函数 sui client call [OPTIONS] --package <package id> --module <module名称> --function <函数名> --gas-budget <GAS_BUDGET> --args <参数1> <参数2> #调用泛型函数,必须指定所有的类型参数否则会报错 sui client call [OPTIONS] --package <package id> --module <module名称> --function <函数名> --gas-budget <GAS_BUDGET> --type-args <类型参数1> <类型参数2> --args <参数1> <参数2>
这里--type-args指定函数传参使用的范型类型,需要指出例如下面函数中T的具体类型是什么
public fun testfunc<T: key+store>(...){ }
查explorer时一般看到的是object的具体类型,可以从object的具体类型中获取到抽象类的具体类型
例如&mut Escrow<T>具体类型为0x29be01a1846f7fd2021df79d25901252627f6afc37bbf4346df92c5b59794da3::swap::Escrow<0x2::coin::Coin<0x84e292b593d459c55eb60e6fc8d7cbe93fb8b9720d4fd47f1a8ead5d54e132d2::AYOUNGCSCOIN::AYOUNGCSCOIN>>,抽象类T具体类型为0x2::coin::Coin<0x84e292b593d459c55eb60e6fc8d7cbe93fb8b9720d4fd47f1a8ead5d54e132d2::AYOUNGCSCOIN::AYOUNGCSCOIN>
有时候要自己搞出来抽象类具体类型,sui就是0x2,类似地其他包里定义的要指定地址
另外多个抽象类 按照函数定义顺序依次指定
更多sui cli 使用https://learnblockchain.cn/article/7766
查看object
sui client objects sui client objects <ADDR> sui client object <OBJECT_ID>
语法
Struct
只有模块内才能访问结构体字段,模块外结构体字段是不可见的 要外部可读 实现getter方法
Object
对象在Sui上存储,维护了一个全局的Map数据结构 Map<ID,object>
必须有key能力
第一个字段是id,类型sui::object::UID
为 Sui 对象创建新对象的唯一方法UID是调用object::new,该函数将当前事务上下文作为生成唯一 ID 的参数
Object ownership
每个对象都有一个owner字段,有4种不同类型的所有权
address-owned objects
由一个地址拥有 使用下面函数之一创建
public fun transfer<T: key>(obj: T, recipient: address) public fun public_transfer<T: key + store>(obj: T, recipient: address)
自定义transfer策略,用sui::transfer::transfer
有store能力,用sui::transfer::public_transfer
访问adress-owned obj:
- 所有者对应object id,则必须在transaction执行期间使用
Transfer to Object中定义的机制访问并动态验证它 - 所有者对应签名派生的地址(账户地址),可以在执行transaction期间将其左右拥有的对象直接使用和访问,其他地址不能在transaction中以任何方式访问
Immutable objects
不可变对象是不能被改变、转移或删除的,没有所有者,任何人都可以使用
下面函数将一个对象转变为不可变对象,操作不可逆
public native fun public_freeze_object<T: key>(obj: T);
只能将不可变对象作为只读、不可变的引用&T传递给函数
test_scenario::take_immutable<T>获取
test_scenario::return_immutable返回
test_scenario::has_most_recent_for_sender对不可变对象返回false
shared object
用sui::transfer::share_object共享,都可以访问,需要key能力
sui::transfer::share_object创建共享对象
需要共识来排序读取和写入
Wrapped Objects
要在sui对象结构(有key能力)嵌入一个结构体类型,该结构体类型要有store能力
swap
struct SwapRequest has key { id: UID, owner: address, object: Object, fee: Balance<SUI>, }
swap请求
public fun request_swap( object: Object, fee: Coin<SUI>, service: address, ctx: &mut TxContext, ) { assert!(coin::value(&fee) >= MIN_FEE, EFeeTooLow); let request = SwapRequest { id: object::new(ctx), owner: tx_context::sender(ctx), object, fee: coin::into_balance(fee), }; transfer::transfer(request, service) }
之后第三方调用execute_swap
public fun execute_swap(s1: SwapRequest, s2: SwapRequest): Balance<SUI>;
然后unpack,检查,转移,删除SwapRequest对象,最后返回费用
let SwapRequest {id: id1, owner: owner1, object: o1, fee: fee1} = s1; let SwapRequest {id: id2, owner: owner2, object: o2, fee: fee2} = s2; assert!(o1.scarcity == o2.scarcity, EBadSwap); assert!(o1.style != o2.style, EBadSwap); transfer::transfer(o1, owner2); transfer::transfer(o2, owner1); object::delete(id1); object::delete(id2); balance::join(&mut fee1, fee2); fee1
例子:https://github.com/MystenLabs/sui/tree/main/examples/move/trusted_swap
函数可见性
- private: 默认private;只允许同一 module 内的函数获取
- public: 可以被同一 module 内的函数获取,也可以被其他 module 定义的函数获取
friend和public(friend)已被移除 如果想让函数只对package可见(只有指定模块能调用):
module pkg::m { public(package) fun f() { ... } } module pkg::a { // this now works directly fun calls_f() { ... pkg::m::f() ... } }
Entry functions
entry修饰符允许从可编程事务块(Programmable Transaction Block)直接调用函数,作为模块的“入口点”
以这种方式调用时,传给entry函数的参数必须是transaction block的输入,而不是该块中之前的transactions的结果,也不能被该块中先前的transactions修改。entry函数只允许返回具有drop的类型
entry fun call()只能Dapp(RPC)调用
Abilities
- Copy - 被修饰的值可以被复制
- Drop - 被修饰的值在作用域结束时可以被丢弃
- Key - 被修饰的值可以作为键值对全局状态进行访问
- Store - 被修饰的值可以被存储到全局状态
基本类型和内建类型的 abilities 是预先定义好的并且不可改变: integers, vector, addresses 和 boolean 类型的值先天具有 copy,drop 和 store ability
结构体的ability可以指定,需要drop才能被丢弃
One-Time Witness
OTW,一种特殊的类型,保证只有一个实例。满足下面条件,该类型被认为是OTW:
- 名字和模块名字相同,全大写
- 只有drop ability
- 没有字段,或只有一个bool字段
包含它的package被published的时候,该类型的唯一实例被传递给其module的init函数
sui::types::is_one_time_witness 检查类型是否可以用作OTW
eg.
module examples::mycoin { /// Name matches the module name struct MYCOIN has drop {} /// The instance is received as the first argument fun init(witness: MYCOIN, ctx: &mut TxContext) { /* ... */ } }
Event
Move event structure An event object in Sui consists of the following attributes:
- id: JSON object containing the transaction digest ID and event sequence.
- packageId: The object ID of the package that emits the event.
- transactionModule: The module that performs the transaction.
- sender: The Sui network address that triggered the event.
- type: The type of event being emitted.
- parsedJson: JSON object describing the event.
- bcs: Binary canonical serialization value.
- timestampMs: Unix epoch timestamp in milliseconds.
使用event::emit在想要监视的操作触发时触发事件
subscribe事件(以typescript sdk为例)
import { JsonRpcProvider, testnetConnection } from '@mysten/sui.js'; // Package is on Testnet. const provider = new JsonRpcProvider(testnetConnection); const Package = '<PACKAGE_ID>'; const MoveEventType = '<PACKAGE_ID>::<MODULE_NAME>::<METHOD_NAME>'; console.log( await provider.getObject({ id: Package, options: { showPreviousTransaction: true }, }), ); let unsubscribe = await provider.subscribeEvent({ filter: { Package }, onMessage: (event) => { console.log('subscribeEvent', JSON.stringify(event, null, 2)); }, }); process.on('SIGINT', async () => { console.log('Interrupted...'); if (unsubscribe) { await unsubscribe(); unsubscribe = undefined; } });
响应返回:
subscribeEvent { "id": { "txDigest": "HkCBeBLQbpKBYXmuQeTM98zprUqaACRkjKmmtvC6MiP1", "eventSeq": "0" }, "packageId": "0x2d6733a32e957430324196dc5d786d7c839f3c7bbfd92b83c469448b988413b1", "transactionModule": "coin_flip", "sender": "0x46f184f2d68007e4344fffe603c4ccacd22f4f28c47f321826e83619dede558e", "type": "0x2d6733a32e957430324196dc5d786d7c839f3c7bbfd92b83c469448b988413b1::coin_flip::Outcome", "parsedJson": { "bet_amount": "4000000000", "game_id": "0xa7e1fb3c18a88d048b75532de219645410705fa48bfb8b13e8dbdbb7f4b9bbce", "guess": 0, "player_won": true }, "bcs": "3oWWjWKRVu115bnnZphyDcJ8EyF9X4pgVguwhEtcsVpBf74B6RywQupm2X", "timestampMs": "1687912116638" }
On-Chain Randomness
entry fun roll_dice(r: &Random, ctx: &mut TxContext): Dice { let generator = new_generator(r, ctx); // generator is a PRG Dice { value: random::generate_u8_in_range(&mut generator, 1, 6) } }
为了安全访问随机:
- 定义函数(private)
entry - 生成随机数时,建议使用函数级别
RandomGenerator,避免状态变量收到其他合约的影响 - 异常情况(unhappy path)消耗的gas不应超过正常情况(happy path)
要使用entry修饰,否则攻击者可以部署合约直接进行extract,返回空则提取失败,触发异常从而造成transaction revert,猜错就中止交易退回手续费
即使函数定义为entry play_dice(guess: u8, fee: Coin<SUI>, r: &Random, ctx: &mut TxContext): Option<GuessedCorrectly> { … },攻击者可以构造PTB攻击
发布一个函数
public fun attack(output: Option<GuessedCorrectly>): GuessedCorrectly { option::extract(output) }
然后发送一个PTB,包含两个指令:play_dice(...)和attack(Result(0))。Result(0)是第一个指令play_dice的返回结果 由于PTB是原子执行的,如果猜测失败,play_dice支付的手续费会被全部revert回去,攻击者不会损失任何费用
为了防止这种基于PTB的攻击,Sui引入了一个新的限制: 如果一个PTB中,在使用了Random作为输入的MoveCall指令之后,还包含了非TransferObjects或MergeCoins的其他指令,Sui将拒绝执行该PTB
Move编译器会拒绝public的函数将RandomGenerator作为参数类型,确保RandomGenerator只能在模块内部使用,不被外部代码访问
要让happy path的gas更高,否则如果happy path的gas比unhappy path 的低,攻击者提供gas只cover happy path,则结果只会是win或者revert transaction(且不会失去支付的费用)
Profile a transaction可以验证不同flow的成本
Dynamic (Object) Fields
使用object字段存储原始数据和其他对象(wrapping)的限制:
- object有一组有限的字段,由publish模块时固定的标识符作为关键字(仅限于struct定义)
- object可能因为wrap了一些其他object变得很大,造成gas fee变高。另外object的size有上限
- 有一些存储不同类型对象的集合的场景,Move中
vector必须用一个类型<T>实例化,不适用
dynamic field:具有任意名称(不仅是identifier),可以动态添加和删除(publish时不固定),仅在访问时影响gas,可以存储不同类型的值
有两种类型动态字段:字段和object字段:
- 字段:可以存储任何具有
store的值,但存储在这种字段的object无法通过其ID使用外部工具(explorer、wallet等)访问存储 - object字段:值必须是objects(具有
key能力,且ID作为第一个字段),但可以通过其ID用外部工具访问
field name可以是任意有key,drop和store的值,包括了所有move primitives和所有内容都具有key,drop和store的struct
添加dynamic field的API:
module sui::dynamic_field { public fun add<Name: copy + drop + store, Value: store>( object: &mut UID, name: Name, value: Value, ); }
module sui::dynamic_object_field { public fun add<Name: copy + drop + store, Value: key + store>( object: &mut UID, name: Name, value: Value, ); }
上述函数为object添加一个名字为name值为value的dynamic field
eg:
use sui::dynamic_object_field as ofield; struct Parent has key { id: UID, } struct Child has key, store { id: UID, count: u64, } public fun add_child(parent: &mut Parent, child: Child) { ofield::add(&mut parent.id, b"child", child); }
上述代码,用childobject为value并使其成为parent的一个名字为b"child"的dynamic filed,造成下面所有权关系:
- sender address仍然拥有
Parentobject Parentobjcet拥有Childobject,且可以通过b"child"指向它
不能覆盖field(尝试添加已定义的相同类型的<name>的值)
可以通过borrow mutably修改field,可以先remove来安全覆盖
访问:
module sui::dynamic_field { public fun borrow<Name: copy + drop + store, Value: store>( object: &UID, name: Name, ): &Value; public fun borrow_mut<Name: copy + drop + store, Value: store>( object: &mut UID, name: Name, ): &mut Value; }
use sui::dynamic_object_field as ofield; public fun mutate_child(child: &mut Child) { child.count = child.count + 1; } public fun mutate_child_via_parent(parent: &mut Parent) { mutate_child(ofield::borrow_mut( &mut parent.id, b"child", )); }
remove dynamic field
module sui::dynamic_field { public fun remove<Name: copy + drop + store, Value: store>( object: &mut UID, name: Name, ): Value; }
被remove的value被使用 eg,被remove的dynamic object field可以被deleted或transfered给一个地址
use sui::dynamic_object_field as ofield; use sui::{object, transfer, tx_context}; use sui::tx_context::TxContext; public fun delete_child(parent: &mut Parent) { let Child { id, count: _ } = reclaim_child(parent); object::delete(id); } public fun reclaim_child(parent: &mut Parent, ctx: &mut TxContext): Child { ofield::remove( &mut parent.id, b"child", ); }
coin
Fungible token
Coin<T>代表开环可替代代币(open-loop fungible tokens),Token<T>代表闭环代币(closed-loop tokens)
由其类型参数T命名
Coin<T>持有的T单位可以与任何其他T单位互换
Treasury capability
用coin::create_currency函数创建coin后,创建coin的合约发布者收到一个TreasuryCap对象,用来mint或burn。TreasuryCap对象可转移
Regulated coins
coin::create_regulated_currency可以创建受监管的coin,函数内部调用coin::create_currency,并返回DenyCapcapability,DenyCapcapability允许维护一个不允许使用tokens的地址列表
无法使用的地址保存在DenyList共享对象;相关操作函数:coin::deny_list_add,coin::deny_list_remove,coin::deny_list_contain
Coin metadata
通常智能合约创建coin时用transfer::public_freeze_object冻结coin的metadata;regulated coin创建时自动冻结其metadata
普通coin对应CoinMetadata对象
regulated coin对应RegulatedCoinMetadata对象,多包含deny list信息
CoinMetadata:id、decimals、name、symbol、description、icon_url
RegulatedCoinMetadata:id、coin_metadata_object、deny_cap_object
Mint
public fun mint<T>( cap: &mut coin::TreasuryCap<T>, value: u64, ctx: &mut tx_context::TxContext ): coin::Coin<T>
函数自动更新TreasuryCap 的总供给量
Burn
public entry fun burn<T>( cap: &mut coin::TreasuryCap<T>, c: coin::Coin<T> ): u64
返回供应量减少的数量
nft
Non-fungible token
动态 NFT(dNFT)
静态 NFT 的迭代,可以根据数据的反馈实时更改 NFT 的数据 dNFT 接受「链上数据」和「链下数据」 链上数据可以通过智能合约直接访问,链下数据则需要由名为「预言机(Oracle)」的实体验证后,再添加到区块链中
ERC21
以太坊上最早也是最基础的NFT底层协议标准。作为一种非同质化代币智能合约标准接口,允许发行基于ERC721的NFT,它规定了NFT资产的最小单位为1、不可拆分且非同质化(独一无二)的特性,ERC721是目前NFT资产的主要规范标准与基础之一(并也为其他链上NFT标准的制定提供了参照),目前以太坊绝大多数NFT都是ERC721标准的
Testing
Test Scenario
https://learnblockchain.cn/article/6409
对于复杂的交易测试,Sui具有test_scenario模块。本模块提供模拟事务、定义发件人和检查事务结果的功能
/// This module contains a dummy store implementation where anyone can purchase /// the same book for any amount of SUI greater than zero. The store owner can /// collect the proceeds using the `StoreOwnerCap` capability. /// /// In the tests section, we use the `test_scenario` module to simulate a few /// transactions and test the store functionality. The test scenario is a very /// powerful tool which can be used to simulate multiple transactions in a single /// test. /// /// The reference for this module is the "Black Books" TV series. module examples::black_books { use sui::sui::SUI; use sui::coin::{Self, Coin}; use sui::balance::{Self, Balance}; /// Trying to purchase the book for 0 SUI. const ECantBeZero: u64 = 0; /// A store owner capability. Allows the owner to collect proceeds. public struct StoreOwnerCap has key, store { id: UID } /// The "Black Books" store located in London. /// Only sells one book: "The Little Book of Calm". public struct BlackBooks has key { id: UID, balance: Balance<SUI>, } /// The only book sold by the Black Books store. public struct LittleBookOfCalm has key, store { id: UID } /// Share the store object and transfer the store owner capability to the sender. fun init(ctx: &mut TxContext) { transfer::transfer(StoreOwnerCap { id: object::new(ctx) }, ctx.sender()); transfer::share_object(BlackBooks { id: object::new(ctx), balance: balance::zero() }) } /// Purchase the "Little Book of Calm" for any amount of SUI greater than zero. public fun purchase( store: &mut BlackBooks, coin: Coin<SUI>, ctx: &mut TxContext ): LittleBookOfCalm { assert!(coin.value() > 0, ECantBeZero); store.balance.join(coin.into_balance()); // create a new book LittleBookOfCalm { id: object::new(ctx) } } /// Collect the proceeds from the store and return them to the sender. public fun collect( store: &mut BlackBooks, _cap: &StoreOwnerCap, ctx: &mut TxContext ): Coin<SUI> { let amount = store.balance.value(); store.balance.split(amount).into_coin(ctx) } // === Tests === #[test_only] // The `init` is not run in tests, and normally a test_only function is // provided so that the module can be initialized in tests. Having it public // is important for tests located in other modules. public fun init_for_testing(ctx: &mut TxContext) { init(ctx); } // using a test-only attibute because this dependency can't be used in // production code and `sui move build` will complain about unused imports. // // the `sui::test_scenario` module is only available in tests. #[test_only] use sui::test_scenario; #[test] // This test uses `test_scenario` to emulate actions performed by 3 accounts. // A single scenario follows this structure: // // - `begin` - starts the first tx and creates the sceanario // - `next_tx` ... - starts the next tx and sets the sender // - `end` - wraps up the scenario // // It provides functions to start transactions, get the `TxContext, pull // objects from account inventory and shared pool, and check transaction // effects. // // In this test scenario: // 1. Bernard opens the store; // 2. Manny buys the book for 10 SUI and sends it to Fran; // 3. Fran sends the book back and buys it herself for 5 SUI; // 4. Bernard collects the proceeds and transfers the store to Fran; fun the_book_store_drama() { // it's a good idea to name addresses for readability // Bernard is the store owner, Manny is searching for the book, // and Fran is the next door store owner. let (bernard, manny, fran) = (@0x1, @0x2, @0x3); // create a test scenario with sender; initiates the first transaction let mut scenario = test_scenario::begin(bernard); // === First transaction === // run the module initializer // we use curly braces to explicitly scope the transaction; { // `test_scenario::ctx` returns the `TxContext` init_for_testing(scenario.ctx()); }; // `next_tx` is used to initiate a new transaction in the scenario and // set the sender to the specified address. It returns `TransactionEffects` // which can be used to check object changes and events. let prev_effects = scenario.next_tx(manny); // make assertions on the effects of the first transaction let created_ids = prev_effects.created(); let shared_ids = prev_effects.shared(); let sent_ids = prev_effects.transferred_to_account(); let events_num = prev_effects.num_user_events(); assert!(created_ids.length() == 2, 0); assert!(shared_ids.length() == 1, 1); assert!(sent_ids.size() == 1, 2); assert!(events_num == 0, 3); // === Second transaction === // we will store the `book_id` in a variable so we can use it later let book_id = { // test scenario can pull shared and sender-owned objects // here we pull the store from the pool let mut store = scenario.take_shared<BlackBooks>(); let ctx = scenario.ctx(); let coin = coin::mint_for_testing<SUI>(10_000_000_000, ctx); // call the purchase function let book = store.purchase(coin, ctx); let book_id = object::id(&book); // send the book to Fran transfer::transfer(book, fran); // now return the store to the pool test_scenario::return_shared(store); // return the book ID so we can use it across transactions book_id }; // === Third transaction === // next transaction - Fran looks in her inventory and finds the book // she decides to return it to Manny and buy another one herself scenario.next_tx(fran); { // objects can be taken from the sender by ID (if there's multiple) // or if there's only one object: `take_from_sender<T>(&scenario)` let book = scenario.take_from_sender_by_id<LittleBookOfCalm>(book_id); // send the book back to Manny transfer::transfer(book, manny); // now repeat the same steps as before let mut store = scenario.take_shared<BlackBooks>(); let ctx = scenario.ctx(); let coin = coin::mint_for_testing<SUI>(5_000_000_000, ctx); // same as before - purchase the book let book = store.purchase(coin, ctx); transfer::transfer(book, fran); // don't forget to return test_scenario::return_shared(store); }; // === Fourth transaction === // last transaction - Bernard collects the proceeds and transfers the store to Fran test_scenario::next_tx(&mut scenario, bernard); { let mut store = scenario.take_shared<BlackBooks>(); let cap = scenario.take_from_sender<StoreOwnerCap>(); let ctx = scenario.ctx(); let coin = store.collect(&cap, ctx); transfer::public_transfer(coin, bernard); transfer::transfer(cap, fran); test_scenario::return_shared(store); }; // finally, the test scenario needs to be finalized scenario.end(); } }
debug
debug::print()可以打印
code examples
Trustless Swap Backend
三阶段:
- A锁定object,并获取锁定的object的key。如果B在第二阶段第二阶段完成前停滞,A可以解锁object来保持liveness
- B注册一个可公开访问的共享
Escrow对象,这也有效地将他们的对象锁定在一个特定的版本,等待A完成swap。B能够要求他们的object返回给他们保持活力 - A把锁定的object和它的key发到共享
Escrow对象。只要下面所有条件满足,swap完成:swap交易的sender是Escrow的接收方;托管中所需对象(exchange_key)的密钥和swap中提供的密钥匹配;swap中提供的密钥解锁Locked<U>
各种报错
Test Scenario中
The value does not have the 'drop' ability and must be consumed before the function returns
take出来的变量在函数结束时没有正确处理,修正代码如下:
{ ts.next_tx(BOB); let mut escrow: Escrow<Coin<SUI>> = ts.take_shared(); let k2: Key = ts.take_from_sender(); let l2: Locked<Coin<SUI>> = ts.take_from_sender(); let c = escrow.swap(k2, l2, ts.ctx()); transfer::public_transfer(c, BOB); ts::return_shared(escrow); // 添加此行 };
另外一个例子 test里创建了一个结构体 结束的时候要consumed掉,例如
transfer::share_object(data);
或官网
let dummy_address = @0xCAFE; transfer::public_transfer(sword, dummy_address);
https://docs.sui.io/guides/developer/first-app/build-test
ran out of gas
测试如果涉及步骤过多可能默认gas不够
sui move test --help发现可以指定gas,搞多一些就够了
letsmove
task2
修改了一下之前写的,share出TreasuryCap让所有人都可以mint
task4
参考Coin Flip写,GameData记录游戏信息,可以通过initial函数初始化,等同于做庄家,得到一个game_data共享对象,玩家可以通过这个共享对象参与游戏,开游戏的creator可以增加奖池(balance),收走奖金,收取手续费 mygame.move里面可以通过start_game参与一局游戏,输入一个0-100的数字并下注,通过finish_game结束游戏,随机数由交易哈希产生,如果guess和随机数差值>50则获胜,玩家下的注和庄家的奖池合并作为所有赌注,赢了收取20%手续费,剩下的给玩家,输了则玩家下的注被加入奖池
task4中将task2的faucet coin作为依赖引入,修改faucet_coin的move.toml,增加published-at = <Address>,并修改[addresses]下的faucet_coin = <Address>,然后task4的move.toml中,[dependencies]内增加faucet_coin = { local = "../../task2/faucet_coin"},之后代码中使用use faucet_coin::AYOUNG_FAUCET_COIN::AYOUNG_FAUCET_COIN;导入
task5
参考untrusted swap实现,并以共享形式实现中间交换对象,在原合约基础上对内部函数进行封装start_swap,create_escrow,end_swap,实现swap。缺点 没有考虑流动性
合约上链:
PackageID: 0xf43d9ca9b12ab76b36654afdb62304e02ebd2bba48621128a72f3ec2cfb85d41
A: start_swap
sui client call --package 0xf43d9ca9b12ab76b36654afdb62304e02ebd2bba48621128a72f3ec2cfb85d41 --module swap --function start_swap --gas-budget 100000000 --type-args "0x2::coin::Coin<0xf3dd827ad2e10db5865d3ab1f0e04dfabd957184959abfdf2dc26d80ccb26306::AYOUNGCSCOIN::AYOUNGCSCOIN>" --args 0x04256532723d640ea6a0e28c66f20ae553f9a7cb764cf46fe92fe2ab7118df31
Key: 0x5a7f83eadb7e8b0a61235832db22e019ba589e1c91dd52c7c5d0a440d152e8bc
Locked: 0xd432681467071b48597e1dd84c185438a9d1f6bcc8007d9714edbfd50449f365
B: create_escrow(参数exchange_key是前面key的id,可以从explorer查)
sui client call --package 0xf43d9ca9b12ab76b36654afdb62304e02ebd2bba48621128a72f3ec2cfb85d41 --module swap --function create_escrow --gas-budget 100000000 --type-args "0x2::coin::Coin<0x4aff5560adba35a7a92864a8f2dfc5e8344f6284fa745861d2c55cbfc60d5340::AYOUNG_FAUCET_COIN::AYOUNG_FAUCET_COIN>" --args 0x08e7951b1533f24e2223cb1d26497453c4a62268f94a1b8ca14d18c108588aa0 0x5a7f83eadb7e8b0a61235832db22e019ba589e1c91dd52c7c5d0a440d152e8bc 0x4ec9567671ffac703a4fa283bb68acdc570974f30e82af3ea147521bfdc593c5
创造了一个shared object
Escrow: 0xd0b27289e211e936e1bf036ed64d651b472a9c16d93dac318500a7b8c3a87873
A: end_swap
sui client call --package 0xf43d9ca9b12ab76b36654afdb62304e02ebd2bba48621128a72f3ec2cfb85d41 --module swap --function end_swap --gas-budget 100000000 --type-args "0x2::coin::Coin<0x4aff5560adba35a7a92864a8f2dfc5e8344f6284fa745861d2c55cbfc60d5340::AYOUNG_FAUCET_COIN::AYOUNG_FAUCET_COIN>" "0x2::coin::Coin<0xf3dd827ad2e10db5865d3ab1f0e04dfabd957184959abfdf2dc26d80ccb26306::AYOUNGCSCOIN::AYOUNGCSCOIN>" --args 0xd0b27289e211e936e1bf036ed64d651b472a9c16d93dac318500a7b8c3a87873 0x5a7f83eadb7e8b0a61235832db22e019ba589e1c91dd52c7c5d0a440d152e8bc 0xd432681467071b48597e1dd84c185438a9d1f6bcc8007d9714edbfd50449f365 0x4ec9567671ffac703a4fa283bb68acdc570974f30e82af3ea147521bfdc593c5
swap完成
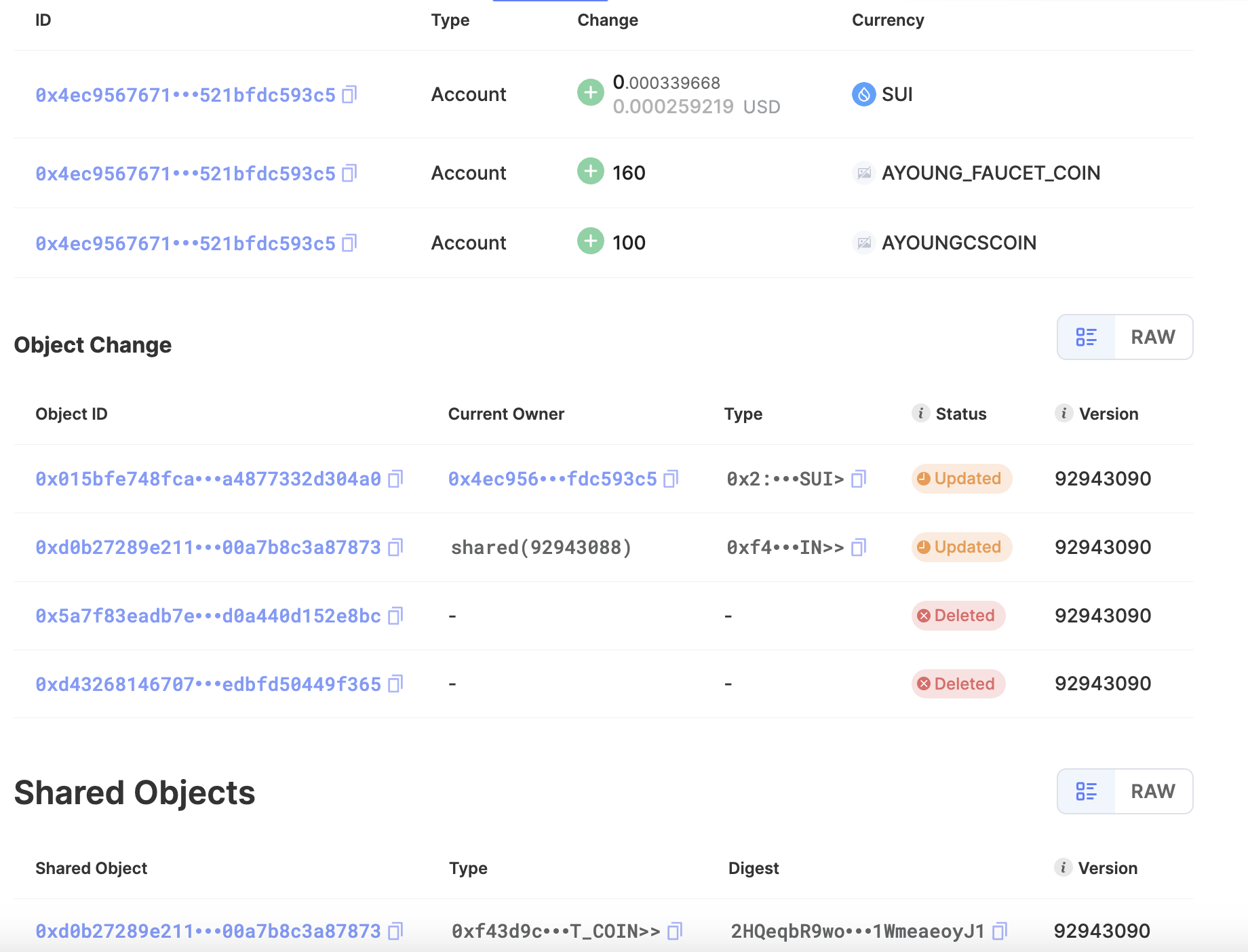
task7
注意bcs编码
task8
注意bcs编码方式,造一个一样的结构体,有key能力的id不能指定,发现可以用address替换编码。事实上bcs编码结构体也是按顺序往后加的,字符串前面会指定长度,无符号数和address啥的会直接加在后面 参考:https://move.sui-book.com/programmability/bcs.html
写test爆破,指定gas上限否则gas不够报错
/// Module: task8 module task8::task8 { use std::ascii::{String, string}; use std::hash; use sui::bcs; public struct Challenge has drop{ iid: address, str: String, difficulity: u64, ture_num: u64 } const Eerror: u64 = 0; #[test_only] use std::debug; #[test] #[expected_failure(abort_code = Eerror)] fun tmp(){ let mut i: u8 = 0; let mut j: u8 = 0; let mut k: u8 = 0; let _sender: address = @0x4ec9567671ffac703a4fa283bb68acdc570974f30e82af3ea147521bfdc593c5; let data = Challenge { iid: @0x19e76ca504c5a5fa5e214a45fca6c058171ba333f6da897b82731094504d5ab9, str: string(b"sXXuT[3Cs2/*^qFSw7;Wj"), difficulity: 3, ture_num: 64 }; while (i<=255){ while (j<=255){ while (k<=255){ let proof : vector<u8> = vector[i , j , k ]; let mut full_proof: vector<u8> = vector::empty<u8>(); vector::append<u8>(&mut full_proof, proof); vector::append<u8>(&mut full_proof, _sender.to_bytes()); vector::append<u8>(&mut full_proof, bcs::to_bytes(&data)); let hash: vector<u8> = hash::sha3_256(full_proof); let mut prefix_sum: u32 = 0; let mut ii: u64 = 0; while (ii < data.difficulity) { prefix_sum = prefix_sum + (*vector::borrow(&hash, ii) as u32); ii = ii + 1; }; if(prefix_sum == 0){ debug::print(&proof); debug::print(&prefix_sum); abort Eerror }; if (k == 255u8) break; k = k+1u8; }; k = 0; if (j == 255u8) break; j = j+1u8; }; j = 0; k = 0; i = i+1u8; }; } }